Essays - Blog Posts

The basics of Research Methods. There’s so much to learn in AS and more is added in the second year. In an exam you could be asked to state which hypothesis is being used in an example, which experimental method would be best for a situation, or to create your own research plan.
5 Things to Probably Never Do on the SAT Essay
Qualifier: Rules are made to be broken, and those below are no exception. Having said that, here are some habits I’d recommend steering clear from on your SAT essay.

1. Probably never use the generic “you.”
Example: “You never know what kind of problems you might get into if you aren’t careful.”
Why this sentence isn’t great: It’s informal, and pretty general.
What to do instead: use “one” in place of “you.” As in, “One never knows what kind of problems one might get into if not careful.” Or, better yet, rewrite the sentence so you to avoid referring to an ambiguous, hypothetical person.
2. Probably never begin an essay with the words “Throughout history…”
Example: “Throughout history, many people have had many different beliefs.”
Why this sentence isn’t great: Again, it’s too general. There isn’t time enough to discuss all recorded history in 25 minutes. So don’t try.
What to do instead: Limit the scope of your argument. Start small, specific. (I’m not going to rewrite the sentence above, as it’d be better to delete it and re-think how to set up the thesis.)
3. Probably avoid generalizations and extreme language.
Example: “Horrible things happen to high school students all the time and they remember those things forever.”
Why this sentence isn’t great: Generalizations like this tend to be either impossible to prove or just plain wrong.
What you can do instead: Qualify your statement, which means to “limit,” “modify” or, as I like to say, “dial it back.”
Rewritten Example: “Certain negative high school experiences are likely to leave a lasting impression.” (Notice how “all” becomes “certain,” I’ve added “likely” and “forever” becomes “lasting impression.”)
A few more words on “qualifying” (because it’s really super important):
We tend to think of “qualifying” as “being eligible” for something. It sometimes mean that, but not here. In this case, I mean taking extreme words and limiting or restricting them. Examples:
Extreme word → Qualified version
“all” → “some” or “certain”
“everyone” → “many people” or better yet, “some people”
“always” → “often,” “in some cases,” “sometimes”
“never” → “rarely” or “seldom”
A few more examples: “My brother is always throwing things at people.” (or) “All men are evil.”
Why these sentences aren’t great: Because these statements aren’t true. And they’re impossible to prove. Read them again and imagine them literally.
Then imagine the evidence you’d need to prove them.
What you can do instead: Qualify ‘em! Dial ‘em back! “My little brother sometimes likes to throw things at people.” (or) “Some argue that all humans have the capacity to do evil.”
*Fun fact: Notice anything about the title of this blog post? #takingmyownadvice
4. Probably never use a hypothetical example.
Example: “When someone says something bad about you it’s like they’re judging you without knowing you.”
What’s not great about this sentence: A few things:
The generic “you.”
It’s general.
It’s a hypothetical example. In other words, it’s not citing something specific that actually happened, so it doesn’t really count as evidence.
What you can do instead: Write about something specific that actually happened. “Last week, when my friend Jac told me that the way I was dressed was “way too preppy,” I felt as if I were being judged.” See how specific?
5. Probably never cite facts without proving them.
Example: “The world is getting more peaceful every day.”
What’s not great about this sentence: Is that true? Can you prove it? How?
What you can do instead: Again, get more specific.
Rewritten example: “Using statistical analysis, psychologist Steven Pinker has argued that the gradual decrease of military conflict, genocide, homicide, torture, and other acts of violence over the last few centuries has led to the present era being the most peaceful time in human history.”
Here’s one more:
Unfounded claim: “You have to see and hear something to learn about it.”
Rewritten: “Last year in my AP Psych class we read an article that discussed a study in which some participants received information both visually and aurally while others received the same information only visually or aurally. It turned out that those who received both kinds of information were 20% more likely to retain that information a year later.”
Written by Ethan Sawyer

hey everyone! so, after creating a studyblr, i have found so many essay writing resources and since writing (whether or not it’s for academic purposes) is something i and several others struggle with on a daily basis, i decided to put together a bunch of excellent resources in this little masterpost. hope you enjoy (bc writing can be very fun when you feel like you actually know what you’re doing) and hope this helps!
I. ESSAY WRITING
+ where do i start?
how to: brainstorming
how to write an outline
essay checklist
writing an essay, in a nutshell
write a university-level essay
how to write a great essay
how to write a great essay pt. ii
a great ppt by a true lifesaver
+ how do i connect my ideas?
writing transitions
masterpost of transition words
transition words for different purposes
+ different types of essays
narrative essay
expository essay
descriptive essay
literary analysis essay
college application essay
descriptive narrative essay
argumentative/discursive essay
+ tips and advice
general advice
avoiding cliches
for: history essays
for: literature essays
writing ur best college essay
+ even more college essay tips
II. OTHER ACADEMIC WRITING
formatting ur papers
general academic writing tips
planning + writing literature papers
III. RESUME WRITING
+ where do i start?
resume template
guide to writing a good resume
writing a resume when u have 0 xp
+ tips and advice
44 tips
25 tips
IV. WRITING ESSENTIALS
+ tips and advice [for writing in general]
funny little guide to writing well
improve ur writing habits asap
create mind maps to organize ur ideas
+ resources for research
refdesk
webMD
wolfram alpha
google scholar
state health facts
u.s. census bureau
internet public library
the library of congress
the old farmer’s almanac
finding data on the internet
+ grammar/vocab/spelling essentials
the owl [grammar resources from the purdue uni]
tip of my tongue [find a word u can’t remember properly]
hypergrammar
grammar girl
+ revising and editing
hemingway [checks the readability of ur essay]
paperrater [rates ur essays and papers]
autocrit [checks grammatical errors + more]
editing checklist [by grammar girl]
+ citations
citation guide
create a bibliography
citation machine
google cite!!!
+ fun stuff
freerice [donate rice while testing ur vocabulary]
rainymood [listen to the rain]
coffitivity [listen to coffee shop sounds]
rainycafe [combination of rainymood + coffitivity]
find out which author u write like
+ my other masterposts
a complete guide to studying (well)
note-taking
more to come soon!
this entire list includes some of the best writing resources (imo) but feel free to message me in case 1) any of the links are broken, 2) u want me to add on to something, 3) u have a suggestion for a masterpost [i would love that so go ahead and ask if u do] or if u just wanna talk! also, feel free to reblog and add ur own comments/resources. hope this helped someone!!!

writing an essay in college is very different from writing an essay in high school. personally, i write more research/history papers than literary essays (the liberal arts life and curse), so this is going to be a post on how a general research-y essay that has a thesis and arguments.
intro
don’t open with a quote and don’t be overly broad.
avoid generalizations
your intro should address the topic of your essay (ex. the significance of gardens in renaissance society), and then narrow down to what you want to talk about in regards to your topic (ex. the political influence of the Medici gardens during the renaissance)
thesis! it should include the argument you want to make about the narrowed down topic, and three (or however many your class requires) reasons to support it. I like to think of it as W = X + Y + Z.
your thesis explains who, what and why in a concise manner.
body
topic sentences should not be a word for word copy of your thesis.
the order of arguments in your thesis is the order of your paragraphs
depending on the length of your essay, there should be at least two justifications to your argument.
so, just as the intro has a formula, X = A + B, and so forth.
A and B should be backed up with some sources/quotes. don’t forget that if you are quoting from class notes to put either the prof’s last name, or (class notes)
be sure to have clear and concise arguments, don’t be flowery
USE WORDS THAT ARE ACCURATE. thesaurus is great but if you use a word that sounds cool but doesn’t capture the meaning you want to convey then don’t use it, because it may just change the meaning of your argument
quote whatever isn’t yours. it is completely fine if 90% of your sentences are quotes. its weird to get used to, but don’t worry about it.
conclusion
the worst part in my opinion.
synthesize don’t summarize. show how your arguments relate back to the thesis.
try not to copy paste your thesis into the conclusion, word it so that the readers understands that through XYZ, you were able to conclude and support argument W (referring back to the thesis formula)
do not add any new information, do not add quotes.
your final sentence should tie up the essay in a pretty bow, but try to avoid clichés
protips
when writing the body paragraphs, your ‘weakest’ paragraph should be in the middle, strongest as your last, and the second best as your first.
if you’re stumped on the intro, skip it. write out the body first, then the intro and you’ll be able to concisely word your thesis
think of your essay as an infomercial. your intro is the loud and clear HERES MY PRODUCT, the body is blasting information on why the product is so cool, and the conclusion is the final push for the viewer to buy that product. make your teacher want to agree with your thesis!
use a mix of paraphrase and quotes!
don’t forget your works cited lmao (the MLA Handbook is a gr8 tool, also OWL Purdue)
prime time for essay writing is in the morning or at night, but make sure you edit it meticulously
EDIT ON PAPER NOT ON YOUR SCREEN
stay humble, study hard
hello! for your college prompts, what advice would you give the students who don't really have any outstanding achievements? the ones who didn't join any contests or have any notable experiences to write about :(
Hi, thanks for the question!
Honestly, every experience can be written as notable. It really depends on how you word your answers. Personal stories, like caring for ill siblings can be described as inspiration for students going into the medical field or school art projects, like painting self-portraits can be described as an eye-opening experience in self-reflection for students planning to study arts.
It’s really important to remember that even though high achievements and notable experiences contribute to an individual’s application, it does not necessarily make or break an individual’s profile. This might sound deceptive, but honestly play up your strengths. (You might not think you have any really good ones, but trust me they’re there!) I’d recommend doing a bit of research of your field of interest’s general responsibilities and focusing on any transferable skills that you currently possess that can be detailed in a college essay or application form. Many scholarship and college committees are looking for students willing to think outside the box, identify transferable experiences for field compatibility and show a clear interest in studying at the school of application. The experience is not the important thing, the reflection and lessons learned are what’s most important. If you show evidence of your ability to commit and work diligently, while showing clear signs of potential; schools will definitely be interested in taking you under their wing.
Hobbies can also play a key role in applications, even non-school or organization held ones. As long as you can show evidence of progress (i.e. photography, videos, maybe a participation certificate) for an activity, self-taught instruments or languages are very impressive. Other hobbies such as crafting, machinery or creative writing can also be assets! I suggest making a list of your daily activities and going from there. Sometimes activities that you may not have considered (i.e. cooking, baking, etc) can greatly contribute to an application. Here’s just a couple examples that could possibly be helpful in the formatting of this sort of writing:
Baking (Have you considered baking something for a charity event? Baking a cake or a tray of cookies can add to your application because you can include the title of charity event volunteer and contributor or that you’ve baked to support charity events.)
Blogging (Even Tumblr blogging! As long as you can show evidence of original posts with a socially acceptable theme (I’d recommend “educational (meaning anything you can learn,)” current-event or literature-based content) you can say that you enjoy writing articles in your spare time and host a blog where you contribute original content.)
Travel (Travel a lot with your family or friends? Spin this experience into a cultural exploration activity and focus heavily on personal reflections of your trip. By doing this, you can say that you have a strong interest in sociology, modern anthropology and ancient anthropology.)
It’s never too late to pick up new skills! Keep an eye out for new opportunities to expand your abilities and community involvement and who’s knows maybe you’ll even find an activity you become extremely passionate about! Here’s some other tips to show off your skills:
Use a higher variety of language in writing: This means, use a thesaurus for application writing! A higher language variety shows that a student has a higher linguistic interest. In saying this however, do not change every word in sentences or an obvious pattern such as one-change-per-sentence! Contribute where you feel you can be fancy.
Name-drop: By that meaning, cleverly mention the names of organizations and companies you’ve been involved with. Involvement refers to any sort of assistance with physical evidence. (Remember that baking example I mentioned earlier? Say that the organization in question was Free the Children - you could add Free the Children charity event volunteer and contributor to your application.) Do not call out organizations randomly but strategically - if it just so happens that the charity in question was present and involved then it doesn’t hurt to add that to your application. This shows that a student is well-connected in their communities as well as being apt at networking.
Strategic self-reflection: In detailing how you felt and what you learned, include references to any historical/current events, academic curriculum or personal interest educational content! For example:
As I explore the streets of Greece, I cannot help but appreciate cultural identities that are in constant evolution. Greece, once a centerpiece of economic power now lies in a new era; one of economic uncertainty in the shadows of the growing strength of several new power players - the United States and China.
This shows that a student has high intellectual ability, is good at problem solving and applying their knowledge where it can be used.
ACADEMIC PHRASE BANK MASTERPOST: CONNECTING WORDS FOR ESSAY WRITING
Addition
To begin with,
In the first place,
Firstly,
The first reason
Additionally
Furthermore,
Another reason why
Secondly, Thirdly,
Next,
Pursuing this further,
Also
Lastly, Finally
In the same way,
Comparison
Similarly,
In the same way,
Likewise,
As with,
Equally,
Contrasting
On the same contrary,
However,
Nevertheless,
On the other hand,
Even so
Alternatively
At the same time
Otherwise
Instead
Conversely
Result
Hence
Therefore
Accordingly
Consequently
Thus
As a result
In consequence
For this reason
For this purpose
Time
Meanwhile
Presently
At last
Finally
Immediately
Thereafter
At that time
Eventually
Currently
Subsequently
In the meantime
Importance
Importantly
Especially
Above all
With attention to
Example
For example
For instance
That is
Such as
As revealed by
Illustrated by
Specifically
In particular
For one thing
This can be seen by
An instance of this
Literary
Clarifies
Conveys
Depicts
Demonstrates
Determines
Displays
Emphasizes
Establishes
Explains
Exemplifies
Highlights
Illustrates
Indicates
Potrays
Represents
Shows
Signifies
Suggests
Beginnings/Causes/Effects
Affects
Generates
Ignites
Impacts
Imposes
Influences
Initiates
Introduces
Involves
Launches
Leads to
Presents
Promotes
Prompts
Results in
Summary
In conclusion,
To sum it all up,
To summarize,
In the final analysis
You can see why …
Finally,
To wrap it all up,
Therefore,
In summary,
In short,
In brief,

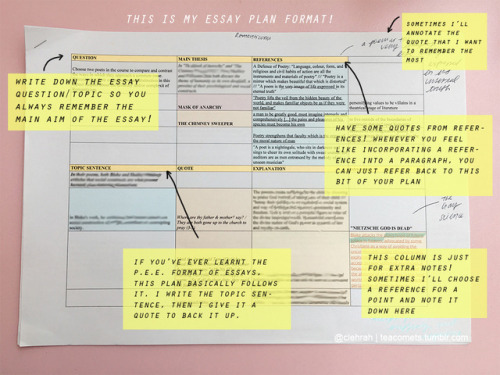







a small guide on how i battle my essays! (click on an image to view it clearer)
(keep in mind: i’m an english major so a majority of my essays are literature-focused!)
these are just some of the methods i want to share that work for me when i write my innumerable amount of essays! i’m definitely a huge planner so it’s no secret that i spend a lot of time on an essay. if you’re a deadline fighter, these tips might not necessarily be helpful (especially the handwriting one). but i hope this gives you an insight on how i write my essays! 🌈


“Talking to yourself can be useful. And writing means being overheard.”
— Zadie Smith, ‘Intimations’


